stripes
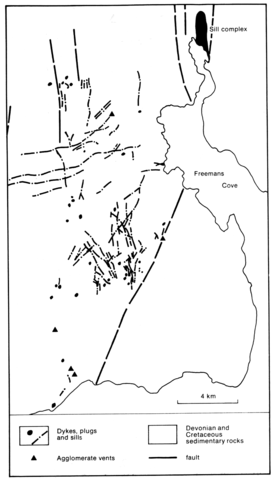
The Freemans Cove suite consists of five agglomerate vents, about 75 dykes and small plugs, as well as several sills, within an area of 40x20 km at the southeast end of Bathurst Island. It is intrusive into Lower and Middle Devonian and Upper Cretaceous sedimentary rocks. Although flows are not now present, lava fragments, bombs and scoria commonly occur as clasts within the agglomerates.. The predominant rock types are nephelinite, basanite, basalt and phonolite. Olivine nephelinites are the most abundant rock type; fresh melilite has been identified from one locality and accessory phlogopite proves to be unusually rich in TiO2 (10%) and BaO (15%). The nephelinites grade into basanites with increase in modal plagioclase (labradorite-andesine). Basalts are the least abundant mafic rocks and both ne and hy-normative varieties are found. Phonolites contain nepheline, alkali feldspar, and in mafic phonolites, pyroxene phenocrysts while large, euhedral amphibole crystals are common. Analyses of these rock types are given by Mitchell and Platt (1984) and for REE by Mitchell and Platt (1983).
MITCHELL, R.H. and PLATT, R.G. 1983. Primitive nephelinitic volcanism associated with rifting and uplift in the Canadian Arctic. Nature, London, 303: 609-12.
MITCHELL, R.H. and PLATT, R.G. 1984. The Freemans Cove volcanic suite: field relations, petrochemistry, and tectonic setting of nephelinite-basanite volcanism associated with rifting in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 21: 428-36.