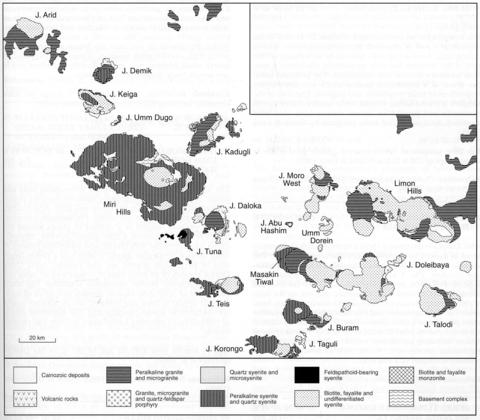
stripes
This complex has an overall length of about 20 km but in the northeastern part is obscured by recent sediments. Biotite microgranite forms a ring-dyke that can be seen clearly on the west of the complex but only sporadically elsewhere; it contains accessory fluorite and tourmaline. The principal intrusive phase is a peralkaline granite which contains varying proportions of sodic amphibole and aegirine. The core of the complex is a subalkaline syenite, while small areas of biotite monzonite and peralkaline quartz syenite have also been identified. Analyses of five rocks are given by Curtis and Lenz (1985).
CURTIS, P. and BRINKMANN, K. 1985. The geology of younger intrusive alkali complexes in the southwestern Nuba Mountains, Sudan. Geologisches Jahrbuch, 63: 3-41.CURTIS, P. and LENZ, H. 1985. Geological and geochronological investigations of selected alkali igneous complexes in the Nuba Mountains, southern Kordofan, Sudan. Geologisches Jahrbuch, 69: 3-24.EL NADI, A.H. 1980. The geology of the Kheig El Kheil, Damik and Umm Dugo igneous complexes, Nuba Mountains, Sudan. M.Sc. thesis, University of Khartoum. (unpublished)