stripes
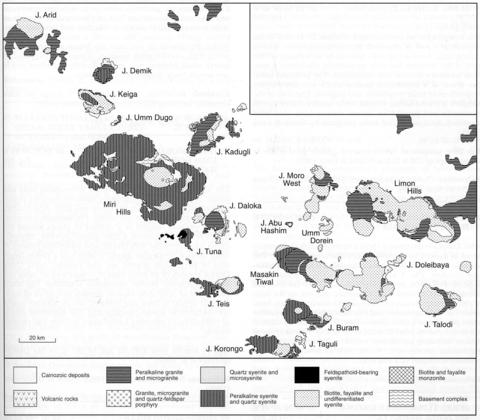
Granitic, dioritic and gabbroic basement gneisses outcrop along the northern and eastern margins of the Jebel Keiga complex. The earliest rocks are intermediate to felsic volcanics which have been subdivided in detail by El Nadi (1980). The dominant, and earliest, intrusive phase is a coarse syenite of perthite, diopside/aegirine-augite, with in some rocks late aegirine, accessory quartz and fluorite. Within this unit is a prominent ring-dyke of a similar syenite but laminated and with biotite and amphibole. There are later units of feldsparphyric microsyenite and a syenite with nepheline, patches of sodalite, aegirine-augite and amphibole. Umm Dugo forms small hills to the southeast of Jebel Keiga and also begins with early felsic pyroclastic rocks which were followed by intrusions of syenite and peralkaline granite, the latter containing sodic amphibole, aegirine and accessory fluorite and zircon. Analyses of four rocks from Jebel Keiga are given by Curtis and Lenz (1985).
CURTIS, P. and BRINKMANN, K. 1985. The geology of younger intrusive alkali complexes in the southwestern Nuba Mountains, Sudan. Geologisches Jahrbuch, 63: 3-41.CURTIS, P. and LENZ, H. 1985. Geological and geochronological investigations of selected alkali igneous complexes in the Nuba Mountains, southern Kordofan, Sudan. Geologisches Jahrbuch, 69: 3-24.EL NADI, A.H. 1980. The geology of the Kheig El Kheil, Damik and Umm Dugo igneous complexes, Nuba Mountains, Sudan. M.Sc. thesis, University of Khartoum. (unpublished)