stripes
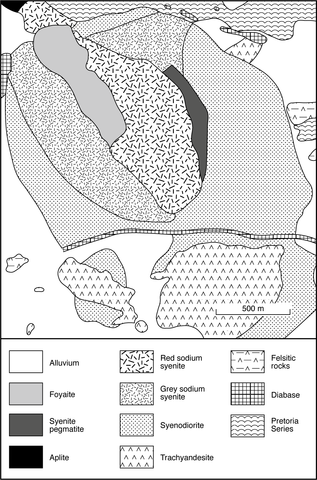
This is an elliptically shaped complex of about 4x2 km which is essentially intrusive but contains some extrusive rocks. An outer ring of syenodiorite is intruded by syenites and foyaites and these are overlain by patches of trachyandesitic lavas xenoliths of which occur in the intrusive rocks. The syenodiorite, referred to as white syenite by Shand (1921), comprises tabular feldspar of oligoclase-andesine cores mantled by alkali feldspar, barkevikitic amphibole and a little sodic amphibole, pale green pyroxene, biotite and accessories including occasional quartz and fluorite. Shand (1921) described a red syenite of 'umptek type' which Toens (1952) mapped as 'grey sodium syenite' and 'red sodium syenite'. These rocks consist of alkali feldspar, including perthite, amphiboles, which may have pyroxene cores, biotite and accessories including rare quartz. In the central area of the complex is a coarse foyaite of alkali feldspar and nepheline in about equal proportions, zoned, deeply coloured aegirine, a sodic amphibole, sodalite and accessory fluorite, titanite, apatite and titanomagnetite. There are small areas of pyroxenite. Dyke rocks include syenite porphyries, foyaite, including a composite dyke, bostonite, tinguaite, jacupirangite, consisting principally of aegirine but with abundant sodalite, ilmenite, titanite and apatite (Shand, 1921) and urtite. The trachyandesitic lavas occupy a ridge across the southern part of the complex and a smaller area in the northeast and consist of feldspar phenocrysts, with oligoclase-andesine cores mantled by alkali feldspar, in a groundmass of feldspar, amphibole, pyroxene, biotite and an opaque phase. Analyses of the principal rock types are given by Shand (1921).
HARMER, R.E. 1985. Rb-Sr isotopic study of units of the Pienaars River alkaline complex, north of Pretoria, South Africa. Transactions of the Geological Society of South Africa, 88: 215-23.OOSTHUYZEN, E.J. and BURGER, A.J. 1964. Radiometric dating of intrusives associated with the Waterberg System. Annals of the Geological Survey of South Africa, 3: 87-104.SHAND, S.J. 1921. The igneous complex of Leeuwfontein, Pretoria District. Transactions of the Geological Society of South Africa, 24: 232-49.TOENS, P.D. 1952. The geology around Leeuwfontein north-east of Pretoria. M.Sc. thesis, University of Pretoria. Unpublished.