stripes
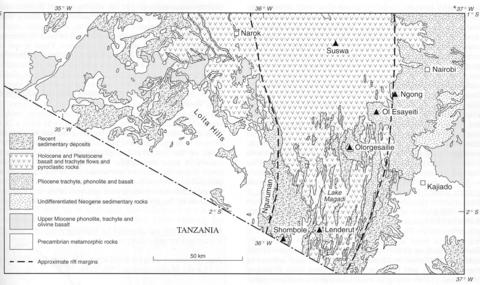
The Ol Esayeiti volcano is located southwest of the Ngong Hills and extends from the southwest corner of the Nairobi map sheet (No. 085-00-062) (Saggerson, 1991) into the Kajiado area to the south (No. 085-00-071) (Matheson, 1966). It comprises flows of phonolite, tephrite and trachyte which partly overlie the products of the Ngong volcano. A phonolite at the base of the succession contains phenocrysts of nepheline, up to 1.5 cm, anorthoclase, titanaugite and titanite set in a groundmass of alkali feldspar, oligoclase, aegirine-augite, aenigmatite and katophorite. The tephrites are typically feldspar-phyric, with oligoclase phenocrysts up to 1.5 cm; ‘barkevikite’ and titanaugite lie in a trachytic matrix of oligoclase, aegirine-augite, nepheline and magnetite.
BAKER, B.H., MITCHELL, J.G. and WILLIAMS, L.A.J. 1988. Stratigraphy, geochronology and volcano-tectonic evolution of the Kedong-Naivasha-Kinangop region, Gregory Rift valley, Kenya. Journal of the Geological Society of London, 145: 107-16.MATHESON, F.J. 1966. Geology of the Kajiado area. Report, Geological Survey of Kenya, 70: 1-51.SAGGERSON, E.P. 1991. Geology of the Nairobi area. Report, Geological Survey of Kenya, 98: 1-91.