stripes
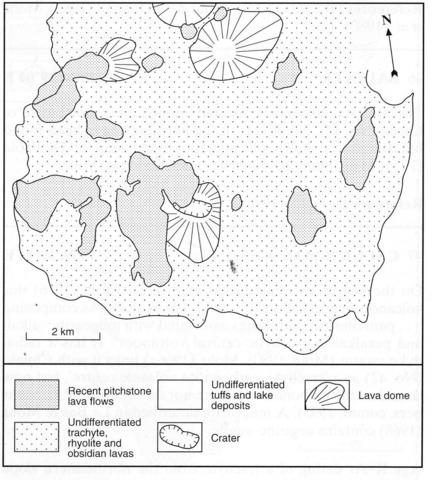
The Alutu volcanic centre lies immediately south of Lake Zwai (Ziway), covers some 90 km2 and rises 650 m above the surrounding lake deposits and tuffs. The volcano consists almost solely of silicic lavas and pumice tuffs but the earlier rocks are obscured by a covering of later pumices there being only weak dissection of the edifice (Dakin and Gibson, 1971). Within the earlier tuffs a 1 km long segment of old caldera wall is visible suggesting the former presence of a large caldera. At a later stage numerous obsidian lavas were erupted that give the volcano a dome-like form, the arcuate disposition of which suggests that they originate along the margins of the old caldera. All the rocks are rhyolitic and contain phenocrysts of quartz and alkali feldspar; mafic phenocrysts include sodic amphibole, green pyroxene, probably ferro-hedenbergite, and aenigmatite. Analyses of two pantelleritic obsidians, including some trace elements, are given by Weaver et al. (1972). The detailed geological map of Abebe et al. (1998) covers part of Alutu and distinguishes four types of pantelleritic units.
ABEBE, B., BOCCALETTI, M., MAZZUOLI, R., BONINI, M., TORTORICI, L. and TRUA, T. 1998. Geological map of the Lake Ziway-Asela region (Main Ethiopian rift). 1:50,000. Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche. DAKIN, F.M. and GIBSON, I.L. 1971. A preliminary account of Alutu, a pantelleritic volcano in the main Ethiopian rift. Bulletin of the Geophysical Observatory, Haile Sellassie I University, Addis Ababa, 13: 110-4.DAKIN, F.M. and GIBSON, I.L. 1971. A preliminary account of Alutu, a pantelleritic volcano in the main Ethiopian rift. Bulletin of the Geophysical Observatory, Haile Sellassie I University, Addis Ababa, 13: 110-4.