stripes
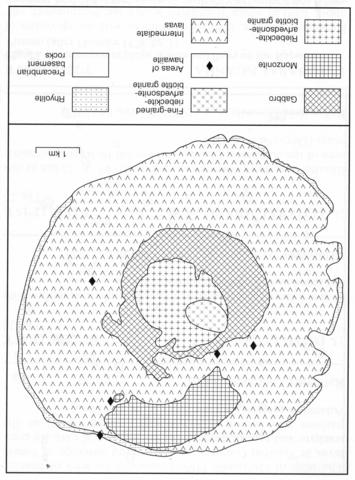
This is a circular, 7.5 km diameter complex consisting of both intrusive and extrusive rocks. The earliest suite is one of olivine gabbros which were followed by monzodiorites and amphibole-biotite monzosyenites and these in turn by a central plug of riebeckite-arfvedsonite-biotite granite, which was itself intruded by a finer grained granite of similar mineralogy. The volcanic rocks, which form an outer circle, include hawaiite, potassic mugearite and benmoreite and alkaline rhyolite. There are radiating dykes of trachyte and spheroidal rhyolite in which pyrochlore has been identified (Lasserre, 1966). Analyses of 10 rocks are given by Deruelle et al. (1991).
DERUELLE, B., MOREAU, C., NKOUMBOU, C., KAMBOU, R., LISSOM, J., NJONFANG, E., GHOGOMU, R.T. and NONO, A. 1991. The Cameroon Line: a review. In A.B. Kampunzu and R.T. Lubala (eds), Magmatism in extensional structural settings. 274-327. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.JACQUEMIN, H., SHEPPARD, S.M.F. and VIDAL, P. 1982. Isotopic geochemistry (O, Sr, Pb) of the Golda Zuelva and Mboutou anorogenic complexes, north Cameroun: mantle origin with evidence for crustal contamination. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 61: 97-111.LASSERRE, M. 1966. Confirmation de l'existence d'une série de granites Tertaires au Cameroun (Afrique équatoriale). Bulletin du Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières. Paris 3: 141-8.LASSERRE, M. 1978. Mise au point sur les granitoides dits "ultimes" du Cameroun: gisement, pétrographie et géochronologie. Bulletin du Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières. Paris, IV: 143-59.