stripes
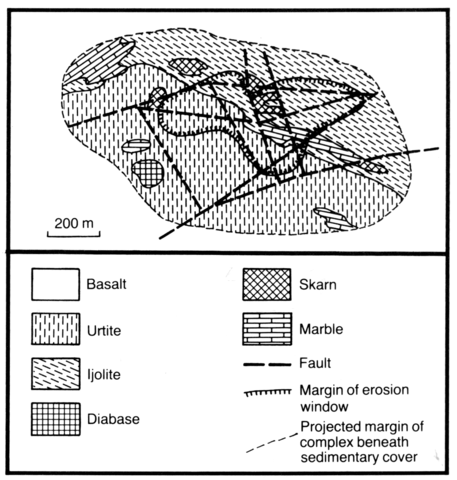
At the present erosion level only a small part (200-400 x 1500 m) of the intrusion can be seen, the rest being hidden beneath a cover of Neogene basalts. Drilling indicates that the intrusion extends over an area of at least 11.5 x 3 km but the margins have not been detected. It is one of the most extensive alkaline intrusions of the region and cuts predominantly marbles and dolomites of Upper Proterozoic age. It comprises various nepheline-pyroxene rocks. In the centre of the massif leucocratic rocks, including urtites, monmouthites and congressites, are dominant, but towards the margins ijolites and melteigites are predominant. Occasionally juvite and nepheline syenite are found. The textures of the urtite and ijolite are hypidiomorphic granular, sometimes with idiomorphic nepheline. These rocks comprise nepheline (10-85%), clinopyroxene (3-65%), which varies widely in composition, amphibole (10%), calcite (1-20%), garnet and titanite (2%). The rocks are partly replaced in places by albite and microcline. Xenoliths of country rock limestones up to about 50 x 100 m have been preserved within the intrusion. Information on the chemical composition of the rocks is available in Sharackshinov (1975) and Andre’E va and Troneva (1986).
ANDRE’E VA, E.D. and TRONEVA, N.V. 1986. Rock-forming minerals of the alkaline rocks from the Vitim Plateau. In: The special features of rock-forming minerals from magmatic rocks. 148-65. Nauka, Moscow.
KONEV, A.A. 1982. Nepheline-bearing rocks from the Sayan-Baikal area. Nauka, Siberian Branch of the Academy of Sciences, Novosibirsk. 201 pp.
SHARACKSHINOV, A.O. 1975. Petrology of nepheline syenite from the Vitim Plateau. Nauka, Siberian Branch of the Academy of Sciences, Novosibirsk. 154 pp.
SHARACKSHINOV, A.O. 1984b. The Mukhal deposit - a new genetic type of nepheline ore. Geologiya Rudnykh Mestorozhdenii, 1: 89-92.