stripes
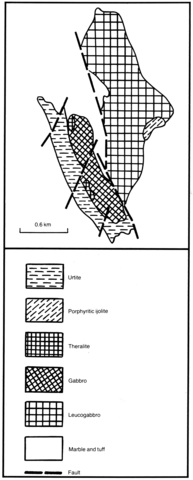
The complex, which has an area of 2.1 km2 and an irregular form, is located along the contact of limestone and volcanic-sedimentary sequences of Lower Cambrian age. The major part, some 75% of the area, is composed of gabbro and leucocratic gabbro with a trachytic texture, which were the first phases to be emplaced. In the southwestern part of the complex an elongate urtite body occurs. Theralite and porphyritic ijolite bodies are also present and the intrusion of urtite was accompanied by metasomatic alteration of the wall rocks, including nephelinization of gabbro and volcanics. Dykes of various compositions including ijolite porphyry, nepheline syenite, micro-ijolite and alkaline syenite, having thicknesses up to 3-4 m, are present in the complex. Also found are dykes of nepheline-pyroxene-pyrrhotite and pyroxene-pyrrhotite rocks, which have been described by Rodygina and Grinev (1989). The urtites have been studied in detail, because of their economic potential, and consist of nepheline (75-90%), fassaite (10-25%) and accessory apatite, pyrrhotite and Fe-Ti oxides. The theralites have equigranular or porphyritic textures amd consist mainly of plagioclase (54%) and fassaite (30%) as well as small quantities of nepheline (8%), olivine (4%), biotite, barkevikite and minor apatite, pyrrhotite and Fe-Ti oxide minerals. The nepheline syenite (foyaite) dykes are composed of microline-perthite, nepheline and aegirine-augite; accessory minerals are represented by lavenite, zircon, titanite, apatite, Fe-Ti oxide and sulphide minerals. The compositions of rocks and minerals are given in publications of Kononova (1976), Andreeva (1968) and Klyushkina et al. (1963).
ANDREEVA, E.D. 1968. Alkaline magmatism of Kuznetsk Alatau. Nauka, Moscow. 169 pp.
KLYUSHKINA, A.V., PRUSEVICH, A.M. and SKOBELEV, Yu.D. 1963. The Kiya-Shaltyr massif of alkaline gabbroids. In I.K. Bazenov and Yu.D. Skobelev (eds) The geology and petrography of nepheline rocks of Kuznetsk Alatau. 46-77. Gosgeoltekhizdat,Moscow.
KONONOVA, V.A. 1976. The Jacupirangite-urtite series of alkaline rocks. Nauka, Moscow. 213 pp.
KONONOVA, V.A. and SHANIN, L.L. 1973. Application of the radiogenic argon method on nepheline for age determinations of alkaline complexes. In G.D. Afanas'ev (ed) Geologic-radiologic interpretation of contradictory age determinations.40-52. Nauka, Moscow.
MOSTOVSKY, A.I. 1978. Formation conditions of alkaline massifs and associated nepheline ores in Kuznetsk Alatau. In V.P. Petrov (ed) Nepheline ore deposits. 66-70. Nauka, Moscow.
*RODYGINA, V.G. and GRINEV, O.M. 1989. Nepheline-pyroxene-pyrrhotite and pyroxene-pyrrhotite rocks of the Kiya-Shaltyr pluton. International Geology Review, 31: 72-8.
SKOBELEV, Yu.D. 1963. The Tuluyul massif of alkaline rocks. InI.K. Bazenov and Yu.D. Skobelev (eds) The geology and petrography of nepheline rocks of Kuznetsk Alatau. 126-34. Gosgeoltekhizdat, Moscow.