stripes
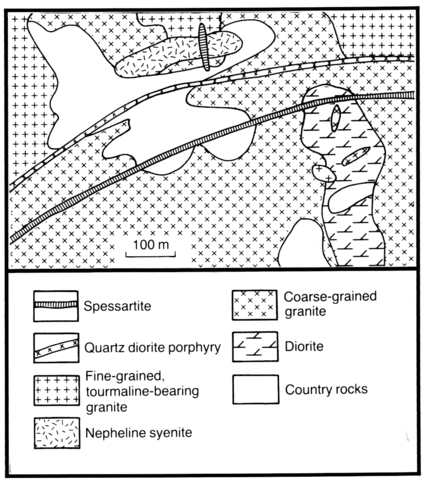
This intrusion is located in Uzbekistan far to the west of the rest of the province (Fig. 88). It has an area of 52 km2, but the two maps (Figs 94 and 95) show only small segments in the northeastern and southeastern parts of the occurrence. It is located within sedimentary rocks, amongst which limestones are predominant, and subordinate extrusive igneous rocks. The country rocks are folded into a large anticline in the axis of which the intrusion was emplaced. Four intrusive phases are present namely: (1) diorite and quartz diorite, (2) coarse-grained biotite granite and granodiorite, (3) peralkaline and nepheline syenites and (4) fine-grained tourmalinised granite. Dyke rocks associated with the syenites are nepheline syenite pegmatite and peralkaline aplite.
KAYUMOV, A.K. and KARABAEV, K.K. 1981. Alkaline magmatism and ore-formation of the south Tyan-Shan. Uzbek Academy of Science Publishers, Tashkent. 135 pp.