stripes
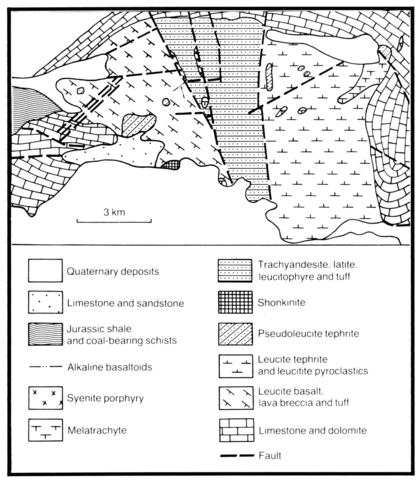
Located in southern Kazakhstan, Daubabinskoye, together with Kaindy (No. 18) and Irisu (No. 19), lies on an east-west-trending deep fracture zone in the Precambrian basement which has been detected geophysically. There are two volcanic sequences within the complex, that have been divided into three fields by faulting. The lowest part of the succession (500 m) is composed of alkaline leucite and analcime trachybasalts and tuffs, together with lavas, breccias and tuffs of leucite tephrite as well as some minor horizons of picritic lavas. The central part of the succession (450 m) consists of leucite-bearing rocks including leucite tephrite and leucitite. These are agglomerates, breccias, tuffs and more rarely lavas. The uppermost section (400 m) is composed of agglomerates and tuffs of trachyandesite and latite that are underlain by agglomerates of leucite-biotite phonolite and trachyte. Both among the extrusive rocks and in the vicinity there are necks and dykes of trachybasalt, leucite tephrite and melanocratic trachyte, as well as stocks of shonkinite porphyry and biotite syenite porphyry. A post-magmatic series of apatite-magnetite rocks (ores) are developed as small dykes. There are zones, some linear, of propilitisation with hematite and copper sulphide mineralisation distributed in the central and western parts of the field. In the southwestern area the alkaline basaltoids have been affected by an intensive post-magmatic zeolitisation.
EREMEEV, N.V. 1984. Volcanic-plutonic complexes of potassic alkaline rocks. Nauka, Moscow. 134 pp.
NURLIBAYEV, A.N. 1973. Alkaline rocks of Kazakhstan and their ore deposits. Nauka, Alma-Ata. 296 pp.
ORLOVA, M.P. 1959. Alkaline basaltoids of the River Daubaba (Tholass Alatau). Information Collection, VSEGEI, Leningrad, 16: 87-95.