stripes
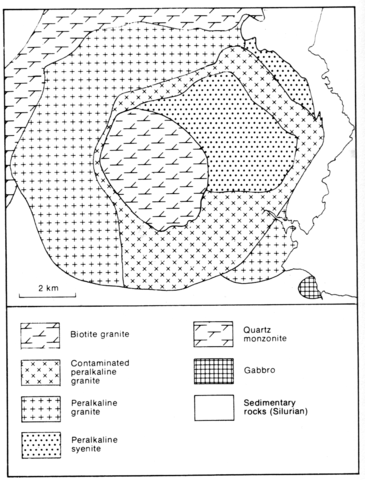
An approximately circular complex some 9 km in diameter, Agamenticus is intruded into Silurian sedimentary rocks and Late Devonian quartz monzonites. The western part of the complex consists of a peralkaline granite of perthite, quartz, arfvedsonite-riebeckite and aegirine-augite, while a homogeneous peralkaline syenite of perthite, less than 2% quartz, the same sodic pyroxenes and amphiboles as the granite, together with accessories, including fayalite, is the dominant rock type in the east. Between the granite and syenite is a ring of variable and heterogeneous quartz syenite which is considered to represent peralkaline granite contaminated by the syenite (Hussey, 1962, p. 41). In the centre of the complex is a plug of porphyritic biotite granite which was probably the last phase of intrusion.
FOLAND, K.A. and FAUL, H. 1977. Ages of the White Mountain intrusives - New Hampshire, Vermont, and Maine, USA. American Journal of Science, 277: 888-904.
HOEFS, J. 1967. A Rb-Sr investigation in the southern York County area, Maine. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1381-15, Fifteenth Annual Progress Report for 1967, U.S. Atomic Energy Commission Contract AT(30-1)-1381, M.I.T.: 127-9.
HUSSEY, A.M. 1962. The geology of southern York County, Maine. Special Geologic Studies Series, Maine Geological Survey, 4: 1-67