stripes
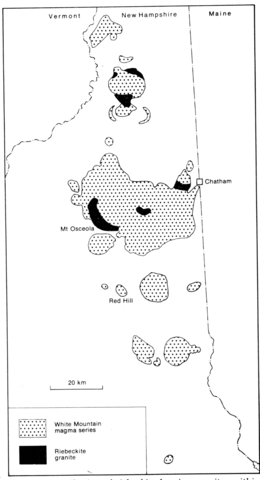
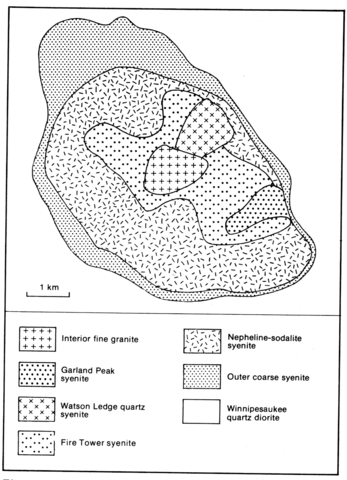
A member of the White Mountain magma series, Red Hill is an oval-shaped multiple intrusion of 17 km2 forming a hill rising to about 420 m above the surrounding lowlands. It is intruded into the Winnipesaukee quartz diorite of late early Devonian age which is metamorphosed for a few metres from the contact. Six units can be distinguished in the complex, the oldest being an outer coarse syenite which is one of three concentrically arranged units. The coarse syenite passes abruptly inwards to a nepheline-sodalite syenite and both units have a laminated fabric of tabular feldspars that dip centripetally at 60-85°. The central part of the complex is a non-foliated syenite which has been intruded by two plugs of quartz syenite and one of granite. The outer coarse syenite is texturally variable and composed of 85-95% perthite, ferrohastingsite and minor aegirine-augite, biotite and quartz or nepheline and sodalite. The nepheline-sodalite syenite is the most extensive unit of the complex and is very variable in grain size and texture. It is composed of tabular perthite, interstitial nepheline and sodalite, often altered to cancrinite, and interstitial ferrohastingsite. The central syenite is relatively homogeneous and apparently chilled against the nepheline-sodalite syenite; it comprises perthite, ferrohastingsite and a little biotite. The more northerly plug of quartz syenite is similar to the central syenite but contains 1-3% quartz, while the other and more southerly syenite plug is finer grained than the rocks of the outer units and has 2-6% quartz. The granite lying in the centre of the complex contains 47-73% microperthite, 3-2% plagioclase (An20-10), 4-7% biotite plus amphibole and 19-29% quartz. Petrography, chemical and modal analyses will be found in Size (1972), and internal textures and structures are discussed in Size (1978). Sr and O isotopes are applied to a petrogenetic discussion of the intrusion by Foland and Friedman (1977).
FOLAND, K.A. and FAUL, H. 1977. Ages of the White Mountain intrusives - New Hampshire, Vermont, and Maine, USA. American Journal of Science, 277: 888-904.
FOLAND, K.A. and FRIEDMAN, I. 1977. Application of Sr and O isotope relations to the petrogenesis of the alkaline rocks of the Red Hill complex, New Hampshire, USA. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 65: 213-25.
SIZE, W.B. 1972. Petrology of the Red Hill syenitic complex, New Hampshire. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 83: 3747-60.
SIZE, W.B. 1978. Textural and structural modification history in the Red Hill layered syenitic complex, New Hampshire. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 89: 1424-8