stripes
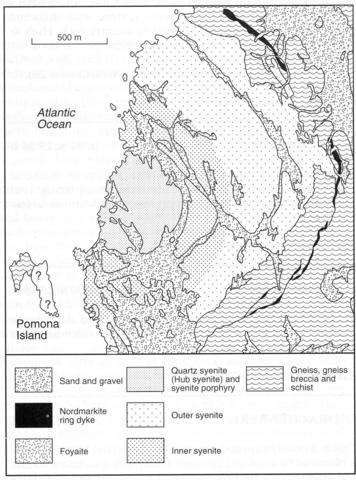
The Pomona complex, the western part of which lies beneath the sea, is about 2.5 km in diameter and intrudes Precambrian granitic and granodioritic gneisses. It consists of concentric outer and inner rings of syenite around a central syenite, with small intrusions of syenite porphyry and nepheline syenite in the core and a narrow concentric dyke of nordmarkite in the gneisses outside the main complex. The broad Outer Syenite (Marsh, 1976) is a coarse rock of perthite, biotite and slightly sodic augite mantled by hastingsitic amphibole. This appears to pass gradationally into the Inner Syenite, although in some areas there appears to be a sharp contact, in which the principal mafic mineral is a sodic ferro-richterite edenite. The central or 'Hub Syenite' consists of perthite, interstitial quartz, sodic ferro-richterite, sodic pyroxene and less common biotite. The Hub Syenite is cut by an irregular intrusion of syenite porphyry and immediately north of the complex bodies of brecciated gneiss occur associated with intrusions of quartz-feldspar porphyry. The ring-dyke of nordmarkite, which is located 100-200 m into the country rocks from the Outer Syenite and dips consistently outwards at 60°, consists of perthite, quartz, minor fluorite, arfvedsonite and magnetite. A small plug of foyaite forms a promontory towards the centre of the complex and is chilled against the Inner Syenite. The foyaite is coarse and of perthite, interstitial nepheline, sodalite and minor cancrinite, with aegirine-augite, a little biotite, Ti-magnetite and commonly fluorite. A well developed radial pattern is defined by dykes which are principally located within the complex but also extend out into the gneisses. The most abundant dykes are bostonites, some of which contain quartz, the mafic minerals being sodic pyroxene or amphibole. Tinguaite dykes are plentiful near the foyaite but lamprophyres are not common. Marsh (1976) gives analyses of all the main rock types.
MARSH, J.S. 1976. The Luderitz alkaline province, South West Africa, III: The Pomona and Drachenberg syenite complexes. Transactions of the Geological Society of South Africa, 79: 168-76.