stripes
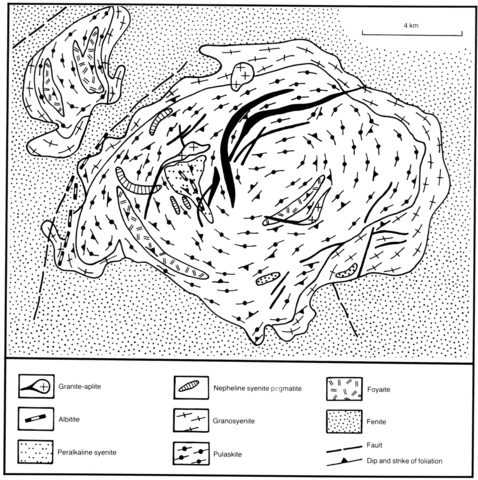
The Burpalinskii alkaline complex occupies an area of about 220 km2 and cuts sedimentary volcanogenic rocks of Proterozoic and Lower Cambrian age. The occurrence has a zoned concentric structure in which, starting granosyenites and quartz syenites, are fine- and medium-grained, massive rocks which towards the centre of the complex are replaced by trachytic varieties. They comprise microcline (80-75%), oligoclase (An28-29; 5-10%), quartz (5-10%), actinolite (5-7%), biotite (2-4%) and occasionally aegirine-diopside, arfvedsonite and accessory titanite and magnetite. In mesocratic varieties the dark-coloured minerals increase up to 25%. The peralkaline syenites and pulaskites are medium- and coarse-grained trachytic rocks of microcline-perthite (85-93%), aegirine-diopside (3-12%), biotite (0-3%), arfvedsonite, zeolitized nepheline, sodalite, albite, ferro-eckermannite and fluorite with minor titanite, ilmenite, zircon and apatite. Among the pulaskites areas of foyaite up to 0.5 x 4 km and sodalite syenite are frequent. The foyaites are trachytic textured rocks consisting of microcline (65-70%), nepheline (12-20%), aegirine-augite (10%) and albite (5%). Pegmatites and dykes are also abundant in the occurrence. Syenite pegmatites are composed predominantly of microcline, aegirine-diopside and arfvedsonite with numerous accessory minerals including manganilmenite, titan-låvenite, caesium-bearing astrophyllite, eudialyte, ferrithorite and catapleite. Pegmatites of nepheline syenite are rare. They comprise microcline at the margins and nepheline-microcline aggregates with arfvedsonite, lepidomelane, ilmenite and eudialyte in central parts. The dyke series is represented by syenite-aplite, tinguaite, solvsbergite, grorudite and lamprophyres. Granites, granite-aplites and granite pegmatites outcropping within the occurrence are of Upper Palaeozoic age and are not likely to be related to the alkaline complex. In hornfelses (fenites) at the outer contacts albitization-aegirinization zones with accessory melanite, cerite, chevkinite, caesium-bearing astrophyllite, sodium catapleite, låvenite and loparite are found, and Merlino et al. (1990) described the new mineral burpalite, a member of the cuspidine-wohlerite-låvenite family, from a fenitized sandstone in the western contact zone.
ANDRE’E V, G.V. 1981. Petrology of the association of the potassium, nepheline and peralkaline syenites. Nauka, Novosibirsk, 85 pp.
ARKHANGELSKAYA, V.V. 1974. Rare-metal alkaline complexes of the southern margin of the Siberian platform. Nedra, Moscow, 128 pp.
*MERLINO, S., PERCHIAZZI, N., KHOMYAKHOV, A.P., PUSHCHAROVSKII, D.Y., KULIKOVA, I.M. and KUZMIN, V.I. 1990. Burpalite, a new mineral from Burpalinski massif, north Transbajkal, USSR: its crystal structure and OD character. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2: 177-85.
PANINA, L.I. 1972. Mineral-genetic characteristic features of some alkaline massifs of the Baikal area. Nauka, Siberian Branch of the USSR Academy of Sciences, Novosibirsk, 127 pp.
ZHIDKOV, A.Ya. 1965. Synnyr and Burpala alkaline intrusives from North Baikal. Ph.D. thesis, University of Leningrad. 210 pp.